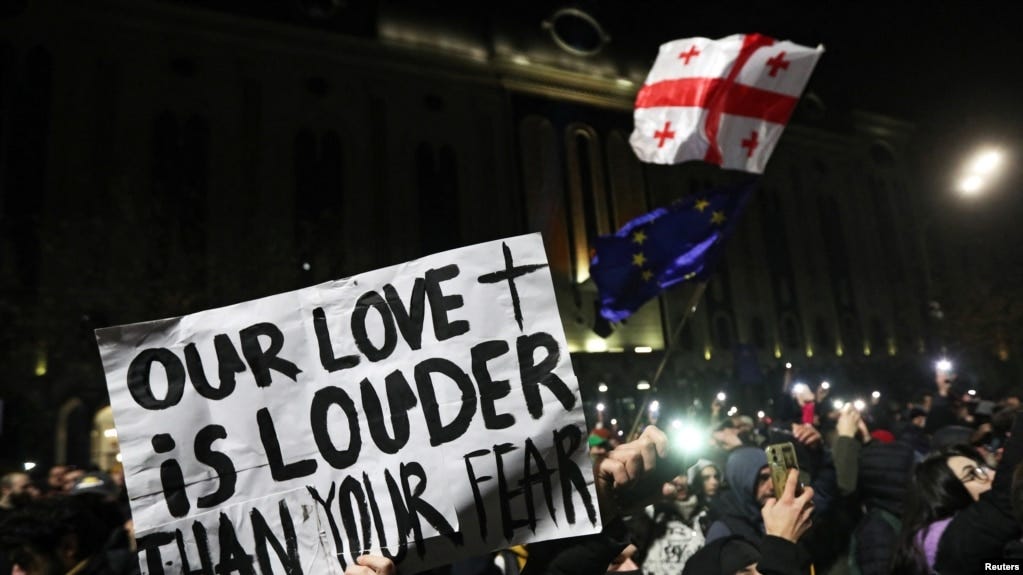Europe is back: EuroHPC's €1.5bn AI Revolution, First AI Factories Are Here
Fueling Europe's Digital Renaissance: €1.5 Billion EuroHPC AI Factories to Drive Innovation and Global Competitiveness
LUNARTECH | Linkedin Vahe | Linkedin Tatev | Youtube LunarTech | X Vahe | X Tatev
Europe Strikes Back: EuroHPC unveils €1.5bn funding for Europe’s first AI factories
Europe is back with Europe AI Factories! The European High Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (EuroHPC) has announced an ambitious €1.5 billion plan to establish AI Factories, marking a transformative step in Europe's digital transformation. These AI Factories are designed to centralize key resources such as supercomputing power, abundant data, and skilled talent, fostering innovation and growth across strategic sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, cybersecurity, and the green economy. By empowering start-ups and SMEs to scale operations and create jobs, this initiative aims to bolster Europe’s global competitiveness in AI-driven technologies while advancing ethical and sustainable solutions to address pressing global challenges.
Startups from around the world, including those with origins outside Europe, stand to benefit from this initiative if they are headquartered within the EU. For instance, an international startup with founders from Asia, Africa, or the Americas, but headquartered in cities like Paris, Berlin, or Madrid, would be eligible to participate in these AI Factories and access their advanced infrastructure and resources. This broad inclusivity underscores the EU’s dedication to fostering a globally collaborative and diverse AI ecosystem, enabling innovative projects from a wide range of cultural and technical backgrounds to thrive within Europe’s digital landscape. Such access offers unparalleled opportunities for startups to leverage cutting-edge computing power and collaborative networks, helping them scale operations and develop transformative AI solutions that could have a global impact.
Strategically located in leading research and technology hubs across Europe, the AI Factories will act as collaboration centers for academia, industry, and policymakers. Sites such as Spain’s BSC AIF, Finland’s LUMI AIF, and Germany’s HammerHAI will host cutting-edge supercomputers optimized for AI, while others will see significant upgrades to their infrastructure. Supported by EU funding through the Digital Europe Programme and Horizon Europe, these investments are expected to double EuroHPC’s computing capacity by 2026. This initiative not only enhances Europe’s position as a global AI leader but also underscores its commitment to using artificial intelligence as a tool for economic prosperity and societal well-being in an increasingly competitive global landscape.
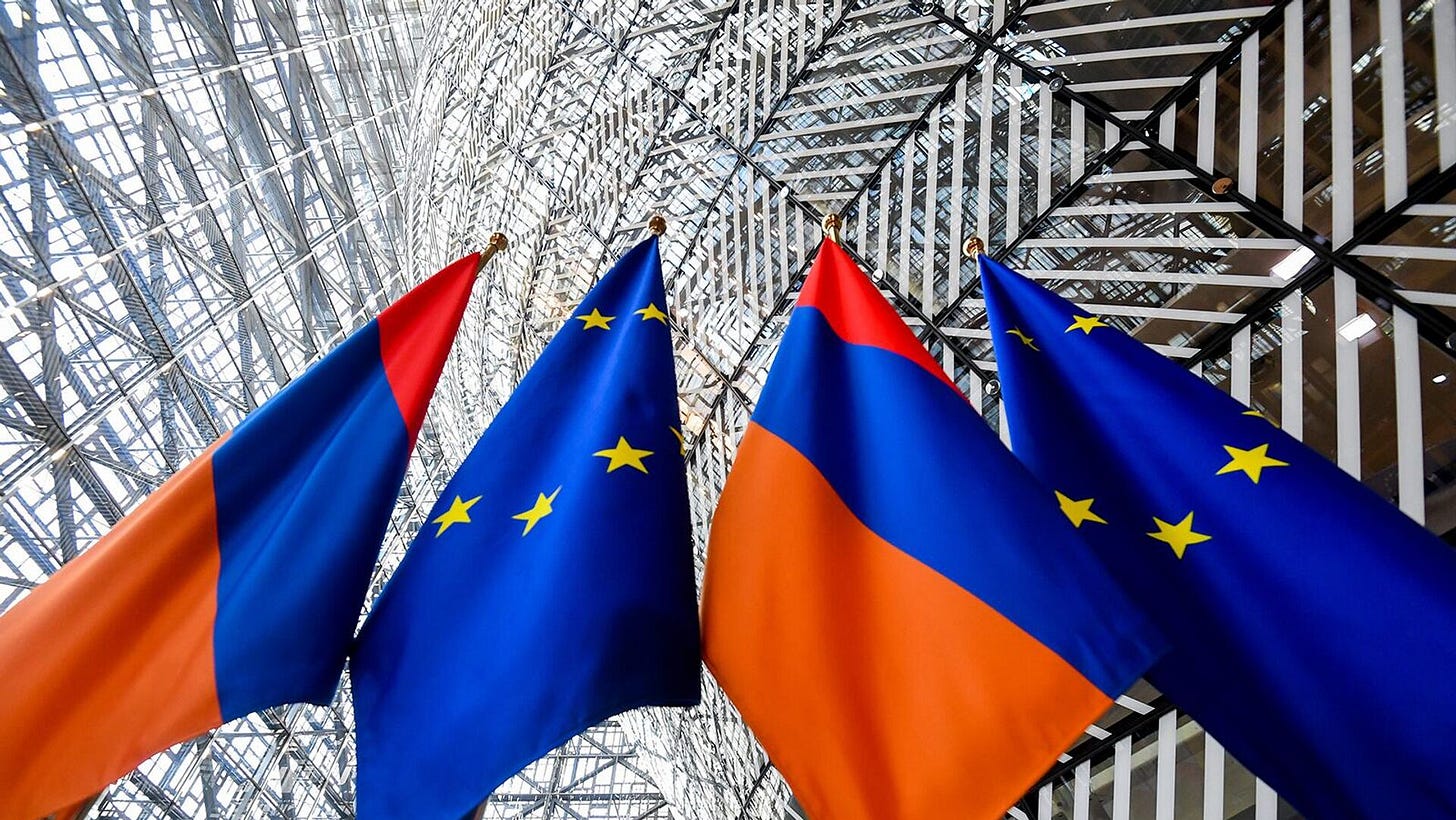
Armenia’s EU Accession Initiative Gains Momentum: Implications for Europe, Armenia, and Global Stability
The Central Electoral Commission (CEC) of Armenia has officially confirmed the validity of signatures submitted by a civic initiative seeking to begin Armenia's accession process to the European Union (EU). The signatures were authenticated using advanced technical and software tools, including cross-referencing signed forms with information in state databases. This thorough verification process highlights the legitimacy of the initiative, reflecting substantial public support and marking a significant step in Armenia's potential pivot towards the EU.
This development carries significant implications for Europe, Armenia, and the global landscape. For Europe, Armenia's potential accession would enhance the EU's geopolitical influence in the strategically vital Caucasus region and strengthen energy and trade connectivity between Europe, Central Asia, and the Middle East. For Armenia, EU membership could bring economic growth, access to European markets, and financial assistance, alongside political and social reforms to strengthen governance and improve citizens' quality of life. Globally, Armenia's move underscores the importance of democratic values, multilateral cooperation, and integration as stabilizing forces in regions facing conflict and power rivalries. This step not only reshapes Armenia's trajectory but also highlights the transformative potential of closer ties between nations and international institutions.
Georgian journalists allege brutal beatings; protests rage against ending EU talks
In Tbilisi, Georgia, a TV journalist and cameraman from the pro-opposition outlet TV Pirveli were targeted by masked men while covering the ongoing pro-EU protests. Reporter Maka Chikhladze and cameraman Giorgi Shetsiruli were attacked during the incident, which occurred on a side street in the capital. The attack took place amidst the 10th consecutive night of mass demonstrations, where thousands have been protesting against the government’s suspension of Georgia’s process to join the European Union. The incident highlights the tensions surrounding the protests and the increasingly challenging environment for journalists in the country.
As Trump 2.0 Scrutinizes Canadian Fentanyl Networks, British Columbia Advances Forfeiture on 14 Properties Linked to Alleged PRC Triad Associate
The British Columbia Civil Forfeiture Office has taken significant steps to seize 14 Vancouver properties linked to transnational money laundering networks, which are believed to fuel North America’s fentanyl crisis. These operations, tied to major criminal organizations, highlight Canada’s challenges in combating global financial crime. U.S. authorities have been increasingly vocal in criticizing Canada for lenient laws and systemic vulnerabilities that enable criminal enterprises to operate with relative ease, further complicating efforts to tackle these networks.
Canadian cities like Vancouver and Toronto have emerged as key hubs for laundering massive amounts of money that support narcotics supply chains involving Mexican cartels and Chinese organized crime groups. Investigations have pointed to Canada’s real estate sector as a prime avenue for laundering proceeds from these operations. Offshore financial hotspots, such as Panama and the Dutch Caribbean islands, play critical roles in these schemes, serving as havens for illicit funds before they are funneled into legitimate markets like Canadian real estate. Although tools like civil forfeiture can freeze suspicious assets, the lack of strict criminal convictions allows these networks to adapt and thrive, perpetuating a cycle of criminal activity.
Vancouver’s global reputation as a money laundering hub and a center for advanced encryption technologies has drawn sharp international scrutiny. Often referred to as the “Dubai of the West,” the city provides a haven for shadowy operations involving Chinese Triads, Mexican cartels, and other international crime syndicates. This dual role—benefiting from illicit investments in local real estate while suffering reputational and public safety costs—has sparked urgent calls for reform. Critics are urging systemic changes, such as implementing anti-racketeering laws and improving intelligence-sharing with the United States, to address Canada’s systemic vulnerabilities and curb the influence of transnational organized crime.
Trump's 'Governor of Canada' Quip Highlights Tense Trade Talks with Trudeau
US President-elect Donald Trump referred to Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau as the "governor" of the "Great State of Canada" in a social media post, following their November meeting at Trump’s Mar-a-Lago estate. During their discussion, Trump reiterated his threat of a 25% tariff on Canadian goods, a move aimed at addressing trade imbalances and ensuring that the U.S. does not disproportionately bear the economic burdens of global trade. This stance is part of Trump’s broader agenda to protect American industries and reduce deficits by holding trade partners accountable for practices he views as exploitative or inefficient.
The proposed tariff also ties into U.S. efforts to tackle cross-border issues, such as drug trafficking, where the country absorbs significant social and economic costs. The U.S. has consistently pushed for stronger preventative measures and shared responsibility in combating these challenges. In response, Trudeau emphasized Canada’s capacity to implement targeted countermeasures, referencing prior actions against U.S. tariffs on steel and aluminum. The discussions underscore a recalibration of trade dynamics, as the U.S. seeks to balance economic responsibilities and address systemic issues with its neighbors and trade partners.
Lukashenko on nuclear weapons in Belarus: Yes, we have it, a few dozen warheads
Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko confirmed that his country possesses tactical nuclear weapons, stating that several dozen warheads have been brought into Belarus. He made this declaration during a discussion with employees of the POZHSNAB company in Borisov, addressing speculation that these weapons were not deployed. Lukashenko emphasized the seriousness of possessing nuclear arms and highlighted their deterrent role, warning that any violation of Belarus’ borders would provoke an immediate and forceful response, potentially involving these weapons. He noted that the agreement to house Russian tactical nuclear weapons was made prior to their deployment.
From Polonez to Optima: New Secret Documents on Belarus-Azerbaijan Military Trade
Hetq’s investigation has documented that Belarus has supplied Azerbaijan with advanced military technology, including the Optima-3.2 jammers capable of disrupting Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) signals such as American GPS and Russian GLONASS. This equipment enables interference with critical navigation and communication networks. Notably, Azerbaijan’s use of such technology has been directed against Armenia, a fellow member of the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO).
Article 1 of the CSTO Treaty, the pact’s foundational provision, establishes that Member States must abstain from the use or threat of force and must settle disputes peacefully. Crucially, it also states that Member States “shall not enter military alliances or take part in any groups of the states, as well as in the actions against other Member State.” By supplying Azerbaijan with technology that directly enhances its capacity to harm the military and strategic interests of Armenia—a CSTO ally—Belarus is not merely failing to prevent aggression; it is actively enabling it. This constitutes a direct violation of the treaty’s most fundamental commitment to mutual defense and peaceful coexistence within the alliance.
The CSTO’s guiding principles are intended to ensure that each member upholds its commitments to collective defense and stability. The clarity of Article 1 leaves little room for alternative interpretations. Belarus’s actions present a direct challenge to the treaty’s stated aim of preventing hostility between its members.
The facts uncovered by Hetq’s investigation indicate a clear conflict between Belarus’s defense cooperation with Azerbaijan and the CSTO’s most fundamental requirements. This development places Belarus’s compliance with the CSTO treaty under scrutiny and raises questions about the alliance’s ability to enforce its own foundational rules.
How the World Turned Its Back on Armenians
Over the past century, Turkey's Armenian population has experienced a dramatic decline, plummeting from approximately 20% of the total population to a mere 0.2%. This significant reduction is primarily attributed to the Armenian Genocide of 1915, during which an estimated 1.5 million Armenians were killed or forcibly displaced by the Ottoman Empire. Subsequent events, such as the population exchanges between Greece and Turkey in 1923 and ongoing emigration due to socio-political pressures, have further diminished the Armenian community within Turkey.
During the Ottoman Empire, Armenians were integral to the empire's economic and administrative systems. They played pivotal roles in various sectors, notably in industry and commerce, and were present in almost every major city. Armenians held significant positions within the Ottoman bureaucracy; for instance, Gabriel Noradunkyan served as Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1912 to 1913, and Agop Kazakyan was Minister of Finance in 1885. Additionally, Armenian families like the Dadians controlled key industries, such as the munitions sector.
Despite their contributions, Armenians faced systemic discrimination and were considered second-class citizens under the millet system, which granted limited autonomy to non-Muslim communities but also imposed restrictions and elevated taxes. This complex relationship underscores the duality of the Armenian experience in the Ottoman Empire: while they were indispensable to its functioning, they simultaneously endured significant hardships.
Today, the Armenian population in Turkey is estimated to be between 40,000 and 60,000 individuals, predominantly residing in Istanbul. Despite being the largest Christian minority in the country, they face challenges related to cultural preservation and religious freedom. The community maintains its heritage through churches, schools, and cultural institutions, striving to sustain its identity amidst a predominantly Muslim society. However, issues such as restrictive government policies and societal discrimination continue to impact the Armenian population's ability to thrive and grow within Turkey.